·
Home ·
News Center ·
News ·
·
Home ·
News Center ·
News ·

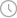 2022.06.17
2022.06.17I. Introduction
The USB interface plays an irreplaceable role in various aspects such as short-distance hardware communication and hardware power supply. Our quality of life has also been improved in the new technology. In addition, with the popularization of USB Type-C technology, USB has once again stood at the forefront. To this end, this article mainly analyzes and explains the development history of USB, USB4.0 line sequence diagram, USB4.0 advantages and other directions.
II. Development of USB Technology
1.USB 1.0
The transmission speed of USB1.0 is only 1.5Mb/s. After hundreds of days and nights of hard work by technicians, USB1.0 was upgraded to USB 1.1 in 1998, and the speed was greatly improved to 12Mb/s. The transmission rate of USB1.1's high-speed transmission mode is 12Mbps, that is, the transmission rate is 1.5MB/s.
2.USB 2.0
The transmission rate of USB2.0 reaches 480Mbps, which is 60MB/s. The driver of USB 2.0 can drive USB1.1 and is compatible with USB1.1.
For our R&D engineers, the main difficulty in designing and developing USB2.0 hardware interface products is that they need to master the complex USB2.0 protocol, develop the driver of USB devices by themselves, and understand the corresponding ARM, FPGA, Linux and other programming.
3.USB 3.0
The maximum transmission rate of USB3.0 under perfect conditions is 5.0Gbps, but in life it can only reach 80% of the limit state value, which is equivalent to 10 times the limit transmission rate of USB 2.0, and the transmission rate is significantly improved. USB3.0 uses 8b/10b encoding at the physical layer, so the maximum transmission rate is 4Gbps, which is less than the transmission rate in the real environment.
4.USB 4.0
The USB4.0 protocol was released in 2019. In terms of hardware interface, the latest generation of USB4.0 uses the Type-C hardware interface. It essentially uses Intel's Thunderbolt 3 technology and also supports USB standards. It is compatible with Thunderbolt 3, USB3.2, USB3.1 and USB2.0 protocols.
As various mobile devices develop towards thinness and portability, and USB4.0 also uses the Type-C interface, the future device interface selection direction will uniformly adopt the Type-C interface of the USB4.0 protocol.
After more than 20 years of development, USB has been upgraded from the initial 1.5Mbps of USB1.0 to today's 40Gbps of USB4.0.